Merge branch 'develop' into check-isam
commit
650bd576ea
|
|
@ -122,21 +122,13 @@ using MotionModel = BetweenFactor<double>;
|
|||
// Test fixture with switching network.
|
||||
/// ϕ(X(0)) .. ϕ(X(k),X(k+1)) .. ϕ(X(k);z_k) .. ϕ(M(0)) .. ϕ(M(K-3),M(K-2))
|
||||
struct Switching {
|
||||
private:
|
||||
HybridNonlinearFactorGraph nonlinearFactorGraph_;
|
||||
|
||||
public:
|
||||
size_t K;
|
||||
DiscreteKeys modes;
|
||||
HybridNonlinearFactorGraph unaryFactors, binaryFactors, modeChain;
|
||||
HybridGaussianFactorGraph linearizedFactorGraph;
|
||||
HybridGaussianFactorGraph linearUnaryFactors, linearBinaryFactors;
|
||||
Values linearizationPoint;
|
||||
|
||||
// Access the flat nonlinear factor graph.
|
||||
const HybridNonlinearFactorGraph &nonlinearFactorGraph() const {
|
||||
return nonlinearFactorGraph_;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* @brief Create with given number of time steps.
|
||||
*
|
||||
|
|
@ -166,37 +158,33 @@ struct Switching {
|
|||
// Create hybrid factor graph.
|
||||
|
||||
// Add a prior ϕ(X(0)) on X(0).
|
||||
nonlinearFactorGraph_.emplace_shared<PriorFactor<double>>(
|
||||
unaryFactors.emplace_shared<PriorFactor<double>>(
|
||||
X(0), measurements.at(0), Isotropic::Sigma(1, prior_sigma));
|
||||
unaryFactors.push_back(nonlinearFactorGraph_.back());
|
||||
|
||||
// Add "motion models" ϕ(X(k),X(k+1),M(k)).
|
||||
for (size_t k = 0; k < K - 1; k++) {
|
||||
auto motion_models = motionModels(k, between_sigma);
|
||||
nonlinearFactorGraph_.emplace_shared<HybridNonlinearFactor>(
|
||||
modes[k], motion_models);
|
||||
binaryFactors.push_back(nonlinearFactorGraph_.back());
|
||||
binaryFactors.emplace_shared<HybridNonlinearFactor>(modes[k],
|
||||
motion_models);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Add measurement factors ϕ(X(k);z_k).
|
||||
auto measurement_noise = Isotropic::Sigma(1, prior_sigma);
|
||||
for (size_t k = 1; k < K; k++) {
|
||||
nonlinearFactorGraph_.emplace_shared<PriorFactor<double>>(
|
||||
X(k), measurements.at(k), measurement_noise);
|
||||
unaryFactors.push_back(nonlinearFactorGraph_.back());
|
||||
unaryFactors.emplace_shared<PriorFactor<double>>(X(k), measurements.at(k),
|
||||
measurement_noise);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Add "mode chain" ϕ(M(0)) ϕ(M(0),M(1)) ... ϕ(M(K-3),M(K-2))
|
||||
modeChain = createModeChain(transitionProbabilityTable);
|
||||
nonlinearFactorGraph_ += modeChain;
|
||||
|
||||
// Create the linearization point.
|
||||
for (size_t k = 0; k < K; k++) {
|
||||
linearizationPoint.insert<double>(X(k), static_cast<double>(k + 1));
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
linearizedFactorGraph =
|
||||
*nonlinearFactorGraph_.linearize(linearizationPoint);
|
||||
linearUnaryFactors = *unaryFactors.linearize(linearizationPoint);
|
||||
linearBinaryFactors = *binaryFactors.linearize(linearizationPoint);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Create motion models for a given time step
|
||||
|
|
@ -227,6 +215,24 @@ struct Switching {
|
|||
}
|
||||
return chain;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/// Get the full linear factor graph.
|
||||
HybridGaussianFactorGraph linearizedFactorGraph() const {
|
||||
HybridGaussianFactorGraph graph;
|
||||
graph.push_back(linearUnaryFactors);
|
||||
graph.push_back(linearBinaryFactors);
|
||||
graph.push_back(modeChain);
|
||||
return graph;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/// Get all the nonlinear factors.
|
||||
HybridNonlinearFactorGraph nonlinearFactorGraph() const {
|
||||
HybridNonlinearFactorGraph graph;
|
||||
graph.push_back(unaryFactors);
|
||||
graph.push_back(binaryFactors);
|
||||
graph.push_back(modeChain);
|
||||
return graph;
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
} // namespace gtsam
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -31,6 +31,7 @@
|
|||
|
||||
// Include for test suite
|
||||
#include <CppUnitLite/TestHarness.h>
|
||||
|
||||
#include <memory>
|
||||
|
||||
using namespace std;
|
||||
|
|
@ -263,7 +264,7 @@ TEST(HybridBayesNet, Choose) {
|
|||
const Ordering ordering(s.linearizationPoint.keys());
|
||||
|
||||
const auto [hybridBayesNet, remainingFactorGraph] =
|
||||
s.linearizedFactorGraph.eliminatePartialSequential(ordering);
|
||||
s.linearizedFactorGraph().eliminatePartialSequential(ordering);
|
||||
|
||||
DiscreteValues assignment;
|
||||
assignment[M(0)] = 1;
|
||||
|
|
@ -292,7 +293,7 @@ TEST(HybridBayesNet, OptimizeAssignment) {
|
|||
const Ordering ordering(s.linearizationPoint.keys());
|
||||
|
||||
const auto [hybridBayesNet, remainingFactorGraph] =
|
||||
s.linearizedFactorGraph.eliminatePartialSequential(ordering);
|
||||
s.linearizedFactorGraph().eliminatePartialSequential(ordering);
|
||||
|
||||
DiscreteValues assignment;
|
||||
assignment[M(0)] = 1;
|
||||
|
|
@ -319,7 +320,7 @@ TEST(HybridBayesNet, Optimize) {
|
|||
Switching s(4, 1.0, 0.1, {0, 1, 2, 3}, "1/1 1/1");
|
||||
|
||||
HybridBayesNet::shared_ptr hybridBayesNet =
|
||||
s.linearizedFactorGraph.eliminateSequential();
|
||||
s.linearizedFactorGraph().eliminateSequential();
|
||||
|
||||
HybridValues delta = hybridBayesNet->optimize();
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -347,7 +348,7 @@ TEST(HybridBayesNet, Pruning) {
|
|||
Switching s(3);
|
||||
|
||||
HybridBayesNet::shared_ptr posterior =
|
||||
s.linearizedFactorGraph.eliminateSequential();
|
||||
s.linearizedFactorGraph().eliminateSequential();
|
||||
EXPECT_LONGS_EQUAL(5, posterior->size());
|
||||
|
||||
// Optimize
|
||||
|
|
@ -400,7 +401,7 @@ TEST(HybridBayesNet, Prune) {
|
|||
Switching s(4);
|
||||
|
||||
HybridBayesNet::shared_ptr posterior =
|
||||
s.linearizedFactorGraph.eliminateSequential();
|
||||
s.linearizedFactorGraph().eliminateSequential();
|
||||
EXPECT_LONGS_EQUAL(7, posterior->size());
|
||||
|
||||
HybridValues delta = posterior->optimize();
|
||||
|
|
@ -418,7 +419,7 @@ TEST(HybridBayesNet, UpdateDiscreteConditionals) {
|
|||
Switching s(4);
|
||||
|
||||
HybridBayesNet::shared_ptr posterior =
|
||||
s.linearizedFactorGraph.eliminateSequential();
|
||||
s.linearizedFactorGraph().eliminateSequential();
|
||||
EXPECT_LONGS_EQUAL(7, posterior->size());
|
||||
|
||||
DiscreteConditional joint;
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -337,7 +337,7 @@ TEST(HybridBayesTree, OptimizeMultifrontal) {
|
|||
Switching s(4);
|
||||
|
||||
HybridBayesTree::shared_ptr hybridBayesTree =
|
||||
s.linearizedFactorGraph.eliminateMultifrontal();
|
||||
s.linearizedFactorGraph().eliminateMultifrontal();
|
||||
HybridValues delta = hybridBayesTree->optimize();
|
||||
|
||||
VectorValues expectedValues;
|
||||
|
|
@ -349,30 +349,40 @@ TEST(HybridBayesTree, OptimizeMultifrontal) {
|
|||
EXPECT(assert_equal(expectedValues, delta.continuous(), 1e-5));
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
namespace optimize_fixture {
|
||||
HybridGaussianFactorGraph GetGaussianFactorGraph(size_t N) {
|
||||
Switching s(N);
|
||||
HybridGaussianFactorGraph graph;
|
||||
|
||||
for (size_t i = 0; i < N - 1; i++) {
|
||||
graph.push_back(s.linearBinaryFactors.at(i));
|
||||
}
|
||||
for (size_t i = 0; i < N; i++) {
|
||||
graph.push_back(s.linearUnaryFactors.at(i));
|
||||
}
|
||||
for (size_t i = 0; i < N - 1; i++) {
|
||||
graph.push_back(s.modeChain.at(i));
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return graph;
|
||||
}
|
||||
} // namespace optimize_fixture
|
||||
|
||||
/* ****************************************************************************/
|
||||
// Test for optimizing a HybridBayesTree with a given assignment.
|
||||
TEST(HybridBayesTree, OptimizeAssignment) {
|
||||
Switching s(4);
|
||||
using namespace optimize_fixture;
|
||||
|
||||
size_t N = 4;
|
||||
|
||||
HybridGaussianISAM isam;
|
||||
HybridGaussianFactorGraph graph1;
|
||||
|
||||
// Add the 3 hybrid factors, x1-x2, x2-x3, x3-x4
|
||||
for (size_t i = 1; i < 4; i++) {
|
||||
graph1.push_back(s.linearizedFactorGraph.at(i));
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Add the Gaussian factors, 1 prior on X(1),
|
||||
// 3 measurements on X(2), X(3), X(4)
|
||||
graph1.push_back(s.linearizedFactorGraph.at(0));
|
||||
for (size_t i = 4; i <= 7; i++) {
|
||||
graph1.push_back(s.linearizedFactorGraph.at(i));
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Add the discrete factors
|
||||
for (size_t i = 7; i <= 9; i++) {
|
||||
graph1.push_back(s.linearizedFactorGraph.at(i));
|
||||
}
|
||||
// Add the 3 hybrid factors, x0-x1, x1-x2, x2-x3
|
||||
// Then add the Gaussian factors, 1 prior on X(0),
|
||||
// 3 measurements on X(1), X(2), X(3)
|
||||
// Finally add the discrete factors
|
||||
// m0, m1-m0, m2-m1
|
||||
HybridGaussianFactorGraph graph1 = GetGaussianFactorGraph(N);
|
||||
|
||||
isam.update(graph1);
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -394,12 +404,13 @@ TEST(HybridBayesTree, OptimizeAssignment) {
|
|||
|
||||
EXPECT(assert_equal(expected_delta, delta));
|
||||
|
||||
Switching s(N);
|
||||
// Create ordering.
|
||||
Ordering ordering;
|
||||
for (size_t k = 0; k < s.K; k++) ordering.push_back(X(k));
|
||||
|
||||
const auto [hybridBayesNet, remainingFactorGraph] =
|
||||
s.linearizedFactorGraph.eliminatePartialSequential(ordering);
|
||||
s.linearizedFactorGraph().eliminatePartialSequential(ordering);
|
||||
|
||||
GaussianBayesNet gbn = hybridBayesNet->choose(assignment);
|
||||
VectorValues expected = gbn.optimize();
|
||||
|
|
@ -410,38 +421,29 @@ TEST(HybridBayesTree, OptimizeAssignment) {
|
|||
/* ****************************************************************************/
|
||||
// Test for optimizing a HybridBayesTree.
|
||||
TEST(HybridBayesTree, Optimize) {
|
||||
Switching s(4);
|
||||
using namespace optimize_fixture;
|
||||
|
||||
size_t N = 4;
|
||||
|
||||
HybridGaussianISAM isam;
|
||||
HybridGaussianFactorGraph graph1;
|
||||
|
||||
// Add the 3 hybrid factors, x1-x2, x2-x3, x3-x4
|
||||
for (size_t i = 1; i < 4; i++) {
|
||||
graph1.push_back(s.linearizedFactorGraph.at(i));
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Add the Gaussian factors, 1 prior on X(0),
|
||||
// 3 measurements on X(2), X(3), X(4)
|
||||
graph1.push_back(s.linearizedFactorGraph.at(0));
|
||||
for (size_t i = 4; i <= 6; i++) {
|
||||
graph1.push_back(s.linearizedFactorGraph.at(i));
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Add the discrete factors
|
||||
for (size_t i = 7; i <= 9; i++) {
|
||||
graph1.push_back(s.linearizedFactorGraph.at(i));
|
||||
}
|
||||
// Add the 3 hybrid factors, x0-x1, x1-x2, x2-x3
|
||||
// Then add the Gaussian factors, 1 prior on X(0),
|
||||
// 3 measurements on X(1), X(2), X(3)
|
||||
// Finally add the discrete factors
|
||||
// m0, m1-m0, m2-m1
|
||||
HybridGaussianFactorGraph graph1 = GetGaussianFactorGraph(N);
|
||||
|
||||
isam.update(graph1);
|
||||
|
||||
HybridValues delta = isam.optimize();
|
||||
|
||||
Switching s(N);
|
||||
// Create ordering.
|
||||
Ordering ordering;
|
||||
for (size_t k = 0; k < s.K; k++) ordering.push_back(X(k));
|
||||
|
||||
const auto [hybridBayesNet, remainingFactorGraph] =
|
||||
s.linearizedFactorGraph.eliminatePartialSequential(ordering);
|
||||
s.linearizedFactorGraph().eliminatePartialSequential(ordering);
|
||||
|
||||
DiscreteFactorGraph dfg = remainingFactorGraph->discreteFactors();
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -461,27 +463,18 @@ TEST(HybridBayesTree, Optimize) {
|
|||
/* ****************************************************************************/
|
||||
// Test for choosing a GaussianBayesTree from a HybridBayesTree.
|
||||
TEST(HybridBayesTree, Choose) {
|
||||
Switching s(4);
|
||||
using namespace optimize_fixture;
|
||||
|
||||
size_t N = 4;
|
||||
|
||||
HybridGaussianISAM isam;
|
||||
HybridGaussianFactorGraph graph1;
|
||||
|
||||
// Add the 3 hybrid factors, x1-x2, x2-x3, x3-x4
|
||||
for (size_t i = 1; i < 4; i++) {
|
||||
graph1.push_back(s.linearizedFactorGraph.at(i));
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Add the Gaussian factors, 1 prior on X(0),
|
||||
// 3 measurements on X(2), X(3), X(4)
|
||||
graph1.push_back(s.linearizedFactorGraph.at(0));
|
||||
for (size_t i = 4; i <= 6; i++) {
|
||||
graph1.push_back(s.linearizedFactorGraph.at(i));
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Add the discrete factors
|
||||
for (size_t i = 7; i <= 9; i++) {
|
||||
graph1.push_back(s.linearizedFactorGraph.at(i));
|
||||
}
|
||||
// Add the 3 hybrid factors, x0-x1, x1-x2, x2-x3
|
||||
// Then add the Gaussian factors, 1 prior on X(0),
|
||||
// 3 measurements on X(1), X(2), X(3)
|
||||
// Finally add the discrete factors
|
||||
// m0, m1-m0, m2-m1
|
||||
HybridGaussianFactorGraph graph1 = GetGaussianFactorGraph(N);
|
||||
|
||||
isam.update(graph1);
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -493,8 +486,9 @@ TEST(HybridBayesTree, Choose) {
|
|||
GaussianBayesTree gbt = isam.choose(assignment);
|
||||
|
||||
// Specify ordering so it matches that of HybridGaussianISAM.
|
||||
Switching s(N);
|
||||
Ordering ordering(KeyVector{X(0), X(1), X(2), X(3), M(0), M(1), M(2)});
|
||||
auto bayesTree = s.linearizedFactorGraph.eliminateMultifrontal(ordering);
|
||||
auto bayesTree = s.linearizedFactorGraph().eliminateMultifrontal(ordering);
|
||||
|
||||
auto expected_gbt = bayesTree->choose(assignment);
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -82,7 +82,7 @@ TEST(HybridEstimation, Full) {
|
|||
// Switching example of robot moving in 1D
|
||||
// with given measurements and equal mode priors.
|
||||
Switching switching(K, 1.0, 0.1, measurements, "1/1 1/1");
|
||||
HybridGaussianFactorGraph graph = switching.linearizedFactorGraph;
|
||||
HybridGaussianFactorGraph graph = switching.linearizedFactorGraph();
|
||||
|
||||
Ordering hybridOrdering;
|
||||
for (size_t k = 0; k < K; k++) {
|
||||
|
|
@ -325,7 +325,7 @@ TEST(HybridEstimation, Probability) {
|
|||
// given measurements and equal mode priors.
|
||||
Switching switching(K, between_sigma, measurement_sigma, measurements,
|
||||
"1/1 1/1");
|
||||
auto graph = switching.linearizedFactorGraph;
|
||||
auto graph = switching.linearizedFactorGraph();
|
||||
|
||||
// Continuous elimination
|
||||
Ordering continuous_ordering(graph.continuousKeySet());
|
||||
|
|
@ -365,7 +365,7 @@ TEST(HybridEstimation, ProbabilityMultifrontal) {
|
|||
// mode priors.
|
||||
Switching switching(K, between_sigma, measurement_sigma, measurements,
|
||||
"1/1 1/1");
|
||||
auto graph = switching.linearizedFactorGraph;
|
||||
auto graph = switching.linearizedFactorGraph();
|
||||
|
||||
// Get the tree of unnormalized probabilities for each mode sequence.
|
||||
AlgebraicDecisionTree<Key> expected_probPrimeTree = GetProbPrimeTree(graph);
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -175,7 +175,7 @@ TEST(HybridBayesNet, Switching) {
|
|||
Switching s(2, betweenSigma, priorSigma);
|
||||
|
||||
// Check size of linearized factor graph
|
||||
const HybridGaussianFactorGraph &graph = s.linearizedFactorGraph;
|
||||
const HybridGaussianFactorGraph &graph = s.linearizedFactorGraph();
|
||||
EXPECT_LONGS_EQUAL(4, graph.size());
|
||||
|
||||
// Create some continuous and discrete values
|
||||
|
|
@ -184,7 +184,7 @@ TEST(HybridBayesNet, Switching) {
|
|||
const DiscreteValues modeZero{{M(0), 0}}, modeOne{{M(0), 1}};
|
||||
|
||||
// Get the hybrid gaussian factor and check it is as expected
|
||||
auto hgf = std::dynamic_pointer_cast<HybridGaussianFactor>(graph.at(1));
|
||||
auto hgf = std::dynamic_pointer_cast<HybridGaussianFactor>(graph.at(2));
|
||||
CHECK(hgf);
|
||||
|
||||
// Get factors and scalars for both modes
|
||||
|
|
@ -298,7 +298,7 @@ TEST(HybridBayesNet, Switching) {
|
|||
factors_x1.push_back(
|
||||
factor); // Use the remaining factor from previous elimination
|
||||
factors_x1.push_back(
|
||||
graph.at(2)); // Add the factor for x1 from the original graph
|
||||
graph.at(1)); // Add the factor for x1 from the original graph
|
||||
|
||||
// Test collectProductFactor for x1 clique
|
||||
auto productFactor_x1 = factors_x1.collectProductFactor();
|
||||
|
|
@ -356,7 +356,7 @@ TEST(HybridGaussianFactorGraph, ErrorAndProbPrime) {
|
|||
Switching s(3);
|
||||
|
||||
// Check size of linearized factor graph
|
||||
const HybridGaussianFactorGraph &graph = s.linearizedFactorGraph;
|
||||
const HybridGaussianFactorGraph &graph = s.linearizedFactorGraph();
|
||||
EXPECT_LONGS_EQUAL(7, graph.size());
|
||||
|
||||
// Eliminate the graph
|
||||
|
|
@ -383,16 +383,16 @@ TEST(HybridGaussianFactorGraph, ErrorAndProbPrime) {
|
|||
TEST(HybridGaussianFactorGraph, DiscreteSelection) {
|
||||
Switching s(3);
|
||||
|
||||
HybridGaussianFactorGraph graph = s.linearizedFactorGraph;
|
||||
HybridGaussianFactorGraph graph = s.linearizedFactorGraph();
|
||||
|
||||
DiscreteValues dv00{{M(0), 0}, {M(1), 0}};
|
||||
GaussianFactorGraph continuous_00 = graph(dv00);
|
||||
GaussianFactorGraph expected_00;
|
||||
expected_00.push_back(JacobianFactor(X(0), I_1x1 * 10, Vector1(-10)));
|
||||
expected_00.push_back(JacobianFactor(X(0), -I_1x1, X(1), I_1x1, Vector1(-1)));
|
||||
expected_00.push_back(JacobianFactor(X(1), -I_1x1, X(2), I_1x1, Vector1(-1)));
|
||||
expected_00.push_back(JacobianFactor(X(1), I_1x1 * 10, Vector1(-10)));
|
||||
expected_00.push_back(JacobianFactor(X(2), I_1x1 * 10, Vector1(-10)));
|
||||
expected_00.push_back(JacobianFactor(X(0), -I_1x1, X(1), I_1x1, Vector1(-1)));
|
||||
expected_00.push_back(JacobianFactor(X(1), -I_1x1, X(2), I_1x1, Vector1(-1)));
|
||||
|
||||
EXPECT(assert_equal(expected_00, continuous_00));
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -400,10 +400,10 @@ TEST(HybridGaussianFactorGraph, DiscreteSelection) {
|
|||
GaussianFactorGraph continuous_01 = graph(dv01);
|
||||
GaussianFactorGraph expected_01;
|
||||
expected_01.push_back(JacobianFactor(X(0), I_1x1 * 10, Vector1(-10)));
|
||||
expected_01.push_back(JacobianFactor(X(0), -I_1x1, X(1), I_1x1, Vector1(-1)));
|
||||
expected_01.push_back(JacobianFactor(X(1), -I_1x1, X(2), I_1x1, Vector1(-0)));
|
||||
expected_01.push_back(JacobianFactor(X(1), I_1x1 * 10, Vector1(-10)));
|
||||
expected_01.push_back(JacobianFactor(X(2), I_1x1 * 10, Vector1(-10)));
|
||||
expected_01.push_back(JacobianFactor(X(0), -I_1x1, X(1), I_1x1, Vector1(-1)));
|
||||
expected_01.push_back(JacobianFactor(X(1), -I_1x1, X(2), I_1x1, Vector1(-0)));
|
||||
|
||||
EXPECT(assert_equal(expected_01, continuous_01));
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -411,10 +411,10 @@ TEST(HybridGaussianFactorGraph, DiscreteSelection) {
|
|||
GaussianFactorGraph continuous_10 = graph(dv10);
|
||||
GaussianFactorGraph expected_10;
|
||||
expected_10.push_back(JacobianFactor(X(0), I_1x1 * 10, Vector1(-10)));
|
||||
expected_10.push_back(JacobianFactor(X(0), -I_1x1, X(1), I_1x1, Vector1(-0)));
|
||||
expected_10.push_back(JacobianFactor(X(1), -I_1x1, X(2), I_1x1, Vector1(-1)));
|
||||
expected_10.push_back(JacobianFactor(X(1), I_1x1 * 10, Vector1(-10)));
|
||||
expected_10.push_back(JacobianFactor(X(2), I_1x1 * 10, Vector1(-10)));
|
||||
expected_10.push_back(JacobianFactor(X(0), -I_1x1, X(1), I_1x1, Vector1(-0)));
|
||||
expected_10.push_back(JacobianFactor(X(1), -I_1x1, X(2), I_1x1, Vector1(-1)));
|
||||
|
||||
EXPECT(assert_equal(expected_10, continuous_10));
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -422,16 +422,16 @@ TEST(HybridGaussianFactorGraph, DiscreteSelection) {
|
|||
GaussianFactorGraph continuous_11 = graph(dv11);
|
||||
GaussianFactorGraph expected_11;
|
||||
expected_11.push_back(JacobianFactor(X(0), I_1x1 * 10, Vector1(-10)));
|
||||
expected_11.push_back(JacobianFactor(X(0), -I_1x1, X(1), I_1x1, Vector1(-0)));
|
||||
expected_11.push_back(JacobianFactor(X(1), -I_1x1, X(2), I_1x1, Vector1(-0)));
|
||||
expected_11.push_back(JacobianFactor(X(1), I_1x1 * 10, Vector1(-10)));
|
||||
expected_11.push_back(JacobianFactor(X(2), I_1x1 * 10, Vector1(-10)));
|
||||
expected_11.push_back(JacobianFactor(X(0), -I_1x1, X(1), I_1x1, Vector1(-0)));
|
||||
expected_11.push_back(JacobianFactor(X(1), -I_1x1, X(2), I_1x1, Vector1(-0)));
|
||||
|
||||
EXPECT(assert_equal(expected_11, continuous_11));
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/* ************************************************************************* */
|
||||
TEST(HybridGaussianFactorGraph, optimize) {
|
||||
TEST(HybridGaussianFactorGraph, Optimize) {
|
||||
HybridGaussianFactorGraph hfg;
|
||||
|
||||
hfg.add(JacobianFactor(X(0), I_3x3, Z_3x1));
|
||||
|
|
@ -451,16 +451,16 @@ TEST(HybridGaussianFactorGraph, Conditionals) {
|
|||
Switching switching(4);
|
||||
|
||||
HybridGaussianFactorGraph hfg;
|
||||
hfg.push_back(switching.linearizedFactorGraph.at(0)); // P(X0)
|
||||
hfg.push_back(switching.linearUnaryFactors.at(0)); // P(X0)
|
||||
Ordering ordering;
|
||||
ordering.push_back(X(0));
|
||||
HybridBayesNet::shared_ptr bayes_net = hfg.eliminateSequential(ordering);
|
||||
|
||||
HybridGaussianFactorGraph hfg2;
|
||||
hfg2.push_back(*bayes_net); // P(X0)
|
||||
hfg2.push_back(switching.linearizedFactorGraph.at(1)); // P(X0, X1 | M0)
|
||||
hfg2.push_back(switching.linearizedFactorGraph.at(2)); // P(X1, X2 | M1)
|
||||
hfg2.push_back(switching.linearizedFactorGraph.at(5)); // P(M1)
|
||||
hfg2.push_back(*bayes_net); // P(X0)
|
||||
hfg2.push_back(switching.linearBinaryFactors.at(0)); // P(X0, X1 | M0)
|
||||
hfg2.push_back(switching.linearBinaryFactors.at(1)); // P(X1, X2 | M1)
|
||||
hfg2.push_back(switching.linearUnaryFactors.at(2)); // P(X2)
|
||||
ordering += X(1), X(2), M(0), M(1);
|
||||
|
||||
// Created product of first two factors and check eliminate:
|
||||
|
|
@ -510,13 +510,13 @@ TEST(HybridGaussianFactorGraph, IncrementalErrorTree) {
|
|||
Switching s(4);
|
||||
|
||||
HybridGaussianFactorGraph graph;
|
||||
graph.push_back(s.linearizedFactorGraph.at(0)); // f(X0)
|
||||
graph.push_back(s.linearizedFactorGraph.at(1)); // f(X0, X1, M0)
|
||||
graph.push_back(s.linearizedFactorGraph.at(2)); // f(X1, X2, M1)
|
||||
graph.push_back(s.linearizedFactorGraph.at(4)); // f(X1)
|
||||
graph.push_back(s.linearizedFactorGraph.at(5)); // f(X2)
|
||||
graph.push_back(s.linearizedFactorGraph.at(7)); // f(M0)
|
||||
graph.push_back(s.linearizedFactorGraph.at(8)); // f(M0, M1)
|
||||
graph.push_back(s.linearUnaryFactors.at(0)); // f(X0)
|
||||
graph.push_back(s.linearBinaryFactors.at(0)); // f(X0, X1, M0)
|
||||
graph.push_back(s.linearBinaryFactors.at(1)); // f(X1, X2, M1)
|
||||
graph.push_back(s.linearUnaryFactors.at(1)); // f(X1)
|
||||
graph.push_back(s.linearUnaryFactors.at(2)); // f(X2)
|
||||
graph.push_back(s.modeChain.at(0)); // f(M0)
|
||||
graph.push_back(s.modeChain.at(1)); // f(M0, M1)
|
||||
|
||||
HybridBayesNet::shared_ptr hybridBayesNet = graph.eliminateSequential();
|
||||
EXPECT_LONGS_EQUAL(5, hybridBayesNet->size());
|
||||
|
|
@ -531,8 +531,8 @@ TEST(HybridGaussianFactorGraph, IncrementalErrorTree) {
|
|||
|
||||
graph = HybridGaussianFactorGraph();
|
||||
graph.push_back(*hybridBayesNet);
|
||||
graph.push_back(s.linearizedFactorGraph.at(3)); // f(X2, X3, M2)
|
||||
graph.push_back(s.linearizedFactorGraph.at(6)); // f(X3)
|
||||
graph.push_back(s.linearBinaryFactors.at(2)); // f(X2, X3, M2)
|
||||
graph.push_back(s.linearUnaryFactors.at(3)); // f(X3)
|
||||
|
||||
hybridBayesNet = graph.eliminateSequential();
|
||||
EXPECT_LONGS_EQUAL(7, hybridBayesNet->size());
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -42,15 +42,15 @@ using symbol_shorthand::Z;
|
|||
|
||||
/* ****************************************************************************/
|
||||
namespace switching3 {
|
||||
// ϕ(x0) ϕ(x0,x1,m0) ϕ(x1,x2,m1) ϕ(x1;z1) ϕ(x2;z2) ϕ(m0) ϕ(m0,m1)
|
||||
// ϕ(x0) ϕ(x1;z1) ϕ(x2;z2) ϕ(x0,x1,m0) ϕ(x1,x2,m1) ϕ(m0) ϕ(m0,m1)
|
||||
const Switching switching(3);
|
||||
const HybridGaussianFactorGraph &lfg = switching.linearizedFactorGraph;
|
||||
const HybridGaussianFactorGraph &lfg = switching.linearizedFactorGraph();
|
||||
|
||||
// First update graph: ϕ(x0) ϕ(x0,x1,m0) ϕ(m0)
|
||||
const HybridGaussianFactorGraph graph1{lfg.at(0), lfg.at(1), lfg.at(5)};
|
||||
const HybridGaussianFactorGraph graph1{lfg.at(0), lfg.at(3), lfg.at(5)};
|
||||
|
||||
// Second update graph: ϕ(x1,x2,m1) ϕ(x1;z1) ϕ(x2;z2) ϕ(m0,m1)
|
||||
const HybridGaussianFactorGraph graph2{lfg.at(2), lfg.at(3), lfg.at(4),
|
||||
const HybridGaussianFactorGraph graph2{lfg.at(4), lfg.at(1), lfg.at(2),
|
||||
lfg.at(6)};
|
||||
} // namespace switching3
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -108,7 +108,7 @@ TEST(HybridGaussianElimination, IncrementalInference) {
|
|||
|
||||
// Now we calculate the expected factors using full elimination
|
||||
const auto [expectedHybridBayesTree, expectedRemainingGraph] =
|
||||
switching.linearizedFactorGraph.eliminatePartialMultifrontal(ordering);
|
||||
switching.linearizedFactorGraph().eliminatePartialMultifrontal(ordering);
|
||||
|
||||
// The densities on X(0) should be the same
|
||||
auto x0_conditional = dynamic_pointer_cast<HybridGaussianConditional>(
|
||||
|
|
@ -162,15 +162,14 @@ TEST(HybridGaussianElimination, Approx_inference) {
|
|||
HybridGaussianFactorGraph graph1;
|
||||
|
||||
// Add the 3 hybrid factors, x0-x1, x1-x2, x2-x3
|
||||
for (size_t i = 1; i < 4; i++) {
|
||||
graph1.push_back(switching.linearizedFactorGraph.at(i));
|
||||
for (size_t i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
|
||||
graph1.push_back(switching.linearBinaryFactors.at(i));
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Add the Gaussian factors, 1 prior on X(0),
|
||||
// 3 measurements on X(1), X(2), X(3)
|
||||
graph1.push_back(switching.linearizedFactorGraph.at(0));
|
||||
for (size_t i = 4; i <= 7; i++) {
|
||||
graph1.push_back(switching.linearizedFactorGraph.at(i));
|
||||
// Add the Gaussian factors, 1 prior on x0,
|
||||
// 3 measurements on x1, x2, x3
|
||||
for (size_t i = 0; i <= 3; i++) {
|
||||
graph1.push_back(switching.linearUnaryFactors.at(i));
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Create ordering.
|
||||
|
|
@ -181,7 +180,7 @@ TEST(HybridGaussianElimination, Approx_inference) {
|
|||
|
||||
// Now we calculate the actual factors using full elimination
|
||||
const auto [unPrunedHybridBayesTree, unPrunedRemainingGraph] =
|
||||
switching.linearizedFactorGraph.eliminatePartialMultifrontal(ordering);
|
||||
switching.linearizedFactorGraph().eliminatePartialMultifrontal(ordering);
|
||||
|
||||
size_t maxNrLeaves = 5;
|
||||
incrementalHybrid.update(graph1);
|
||||
|
|
@ -266,15 +265,14 @@ TEST_DISABLED(HybridGaussianElimination, IncrementalApproximate) {
|
|||
|
||||
/***** Run Round 1 *****/
|
||||
// Add the 3 hybrid factors, x0-x1, x1-x2, x2-x3
|
||||
for (size_t i = 1; i < 4; i++) {
|
||||
graph.push_back(switching.linearizedFactorGraph.at(i));
|
||||
for (size_t i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
|
||||
graph.push_back(switching.linearBinaryFactors.at(i));
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Add the Gaussian factors, 1 prior on X(0),
|
||||
graph.push_back(switching.linearizedFactorGraph.at(0));
|
||||
// 3 measurements on X(1), X(2), X(3)
|
||||
for (size_t i = 5; i <= 7; i++) {
|
||||
graph.push_back(switching.linearizedFactorGraph.at(i));
|
||||
// Add the Gaussian factors, 1 prior on x0,
|
||||
// 3 measurements on x1, x2, x3
|
||||
for (size_t i = 0; i <= 3; i++) {
|
||||
graph.push_back(switching.linearUnaryFactors.at(i));
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Run update with pruning
|
||||
|
|
@ -295,11 +293,9 @@ TEST_DISABLED(HybridGaussianElimination, IncrementalApproximate) {
|
|||
5, incrementalHybrid[X(3)]->conditional()->asHybrid()->nrComponents());
|
||||
|
||||
/***** Run Round 2 *****/
|
||||
graph.resize(0); // clear all factors
|
||||
// Add hybrid factor X(3)-X(4)
|
||||
graph.push_back(switching.linearizedFactorGraph.at(4));
|
||||
// Add measurement factor X(4)
|
||||
graph.push_back(switching.linearizedFactorGraph.at(8));
|
||||
graph = HybridGaussianFactorGraph();
|
||||
graph.push_back(switching.linearBinaryFactors.at(3)); // hybrid x3-x4
|
||||
graph.push_back(switching.linearUnaryFactors.at(4)); // x4
|
||||
|
||||
// Run update with pruning a second time.
|
||||
incrementalHybrid.update(graph);
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -189,8 +189,10 @@ TEST(HybridGaussianProductFactor, AddPruned) {
|
|||
product += prunedFactorB;
|
||||
EXPECT_LONGS_EQUAL(6, product.nrLeaves());
|
||||
|
||||
#ifdef GTSAM_DT_MERGING
|
||||
auto pruned = product.removeEmpty();
|
||||
EXPECT_LONGS_EQUAL(5, pruned.nrLeaves());
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/* ************************************************************************* */
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -249,7 +249,7 @@ TEST(HybridNonlinearFactorGraph, Switching) {
|
|||
Switching self(3);
|
||||
|
||||
EXPECT_LONGS_EQUAL(7, self.nonlinearFactorGraph().size());
|
||||
EXPECT_LONGS_EQUAL(7, self.linearizedFactorGraph.size());
|
||||
EXPECT_LONGS_EQUAL(7, self.linearizedFactorGraph().size());
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/****************************************************************************
|
||||
|
|
@ -276,7 +276,7 @@ TEST(HybridNonlinearFactorGraph, EliminationTree) {
|
|||
for (size_t k = 0; k < self.K; k++) ordering.push_back(X(k));
|
||||
|
||||
// Create elimination tree.
|
||||
HybridEliminationTree etree(self.linearizedFactorGraph, ordering);
|
||||
HybridEliminationTree etree(self.linearizedFactorGraph(), ordering);
|
||||
EXPECT_LONGS_EQUAL(1, etree.roots().size())
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -286,12 +286,12 @@ TEST(HybridNonlinearFactorGraph, EliminationTree) {
|
|||
TEST(GaussianElimination, Eliminate_x0) {
|
||||
Switching self(3);
|
||||
|
||||
// Gather factors on x1, has a simple Gaussian and a hybrid factor.
|
||||
// Gather factors on x0, has a simple Gaussian and a hybrid factor.
|
||||
HybridGaussianFactorGraph factors;
|
||||
// Add gaussian prior
|
||||
factors.push_back(self.linearizedFactorGraph[0]);
|
||||
factors.push_back(self.linearUnaryFactors[0]);
|
||||
// Add first hybrid factor
|
||||
factors.push_back(self.linearizedFactorGraph[1]);
|
||||
factors.push_back(self.linearBinaryFactors[0]);
|
||||
|
||||
// Eliminate x0
|
||||
const Ordering ordering{X(0)};
|
||||
|
|
@ -313,8 +313,8 @@ TEST(HybridsGaussianElimination, Eliminate_x1) {
|
|||
|
||||
// Gather factors on x1, will be two hybrid factors (with x0 and x2, resp.).
|
||||
HybridGaussianFactorGraph factors;
|
||||
factors.push_back(self.linearizedFactorGraph[1]); // involves m0
|
||||
factors.push_back(self.linearizedFactorGraph[2]); // involves m1
|
||||
factors.push_back(self.linearBinaryFactors[0]); // involves m0
|
||||
factors.push_back(self.linearBinaryFactors[1]); // involves m1
|
||||
|
||||
// Eliminate x1
|
||||
const Ordering ordering{X(1)};
|
||||
|
|
@ -349,7 +349,7 @@ GaussianFactorGraph::shared_ptr batchGFG(double between,
|
|||
TEST(HybridGaussianElimination, EliminateHybrid_2_Variable) {
|
||||
Switching self(2, 1.0, 0.1);
|
||||
|
||||
auto factors = self.linearizedFactorGraph;
|
||||
auto factors = self.linearizedFactorGraph();
|
||||
|
||||
// Eliminate x0
|
||||
const Ordering ordering{X(0), X(1)};
|
||||
|
|
@ -380,15 +380,13 @@ TEST(HybridGaussianElimination, EliminateHybrid_2_Variable) {
|
|||
TEST(HybridNonlinearFactorGraph, Partial_Elimination) {
|
||||
Switching self(3);
|
||||
|
||||
auto linearizedFactorGraph = self.linearizedFactorGraph;
|
||||
|
||||
// Create ordering of only continuous variables.
|
||||
Ordering ordering;
|
||||
for (size_t k = 0; k < self.K; k++) ordering.push_back(X(k));
|
||||
|
||||
// Eliminate partially i.e. only continuous part.
|
||||
const auto [hybridBayesNet, remainingFactorGraph] =
|
||||
linearizedFactorGraph.eliminatePartialSequential(ordering);
|
||||
self.linearizedFactorGraph().eliminatePartialSequential(ordering);
|
||||
|
||||
CHECK(hybridBayesNet);
|
||||
EXPECT_LONGS_EQUAL(3, hybridBayesNet->size());
|
||||
|
|
@ -444,11 +442,11 @@ TEST(HybridNonlinearFactorGraph, PrintErrors) {
|
|||
// Get nonlinear factor graph and add linear factors to be holistic.
|
||||
// TODO(Frank): ???
|
||||
HybridNonlinearFactorGraph fg = self.nonlinearFactorGraph();
|
||||
fg.add(self.linearizedFactorGraph);
|
||||
fg.add(self.linearizedFactorGraph());
|
||||
|
||||
// Optimize to get HybridValues
|
||||
HybridBayesNet::shared_ptr bn =
|
||||
self.linearizedFactorGraph.eliminateSequential();
|
||||
self.linearizedFactorGraph().eliminateSequential();
|
||||
HybridValues hv = bn->optimize();
|
||||
|
||||
// Print and verify
|
||||
|
|
@ -465,8 +463,6 @@ TEST(HybridNonlinearFactorGraph, PrintErrors) {
|
|||
TEST(HybridNonlinearFactorGraph, Full_Elimination) {
|
||||
Switching self(3);
|
||||
|
||||
auto linearizedFactorGraph = self.linearizedFactorGraph;
|
||||
|
||||
// We first do a partial elimination
|
||||
DiscreteBayesNet discreteBayesNet;
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -477,7 +473,7 @@ TEST(HybridNonlinearFactorGraph, Full_Elimination) {
|
|||
|
||||
// Eliminate partially.
|
||||
const auto [hybridBayesNet_partial, remainingFactorGraph_partial] =
|
||||
linearizedFactorGraph.eliminatePartialSequential(ordering);
|
||||
self.linearizedFactorGraph().eliminatePartialSequential(ordering);
|
||||
|
||||
DiscreteFactorGraph discrete_fg =
|
||||
remainingFactorGraph_partial->discreteFactors();
|
||||
|
|
@ -495,7 +491,7 @@ TEST(HybridNonlinearFactorGraph, Full_Elimination) {
|
|||
|
||||
// Eliminate partially.
|
||||
HybridBayesNet::shared_ptr hybridBayesNet =
|
||||
linearizedFactorGraph.eliminateSequential(ordering);
|
||||
self.linearizedFactorGraph().eliminateSequential(ordering);
|
||||
|
||||
CHECK(hybridBayesNet);
|
||||
EXPECT_LONGS_EQUAL(5, hybridBayesNet->size());
|
||||
|
|
@ -528,7 +524,7 @@ TEST(HybridNonlinearFactorGraph, Full_Elimination) {
|
|||
TEST(HybridNonlinearFactorGraph, Printing) {
|
||||
Switching self(3);
|
||||
|
||||
auto linearizedFactorGraph = self.linearizedFactorGraph;
|
||||
auto linearizedFactorGraph = self.linearizedFactorGraph();
|
||||
|
||||
// Create ordering.
|
||||
Ordering ordering;
|
||||
|
|
@ -551,6 +547,24 @@ GaussianFactor:
|
|||
No noise model
|
||||
|
||||
Factor 1
|
||||
GaussianFactor:
|
||||
|
||||
A[x1] = [
|
||||
10
|
||||
]
|
||||
b = [ -10 ]
|
||||
No noise model
|
||||
|
||||
Factor 2
|
||||
GaussianFactor:
|
||||
|
||||
A[x2] = [
|
||||
10
|
||||
]
|
||||
b = [ -10 ]
|
||||
No noise model
|
||||
|
||||
Factor 3
|
||||
HybridGaussianFactor:
|
||||
Hybrid [x0 x1; m0]{
|
||||
Choice(m0)
|
||||
|
|
@ -578,7 +592,7 @@ scalar: 0.918939
|
|||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
Factor 2
|
||||
Factor 4
|
||||
HybridGaussianFactor:
|
||||
Hybrid [x1 x2; m1]{
|
||||
Choice(m1)
|
||||
|
|
@ -606,24 +620,6 @@ scalar: 0.918939
|
|||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
Factor 3
|
||||
GaussianFactor:
|
||||
|
||||
A[x1] = [
|
||||
10
|
||||
]
|
||||
b = [ -10 ]
|
||||
No noise model
|
||||
|
||||
Factor 4
|
||||
GaussianFactor:
|
||||
|
||||
A[x2] = [
|
||||
10
|
||||
]
|
||||
b = [ -10 ]
|
||||
No noise model
|
||||
|
||||
Factor 5
|
||||
DiscreteFactor:
|
||||
P( m0 ):
|
||||
|
|
@ -646,16 +642,38 @@ DiscreteFactor:
|
|||
#else
|
||||
string expected_hybridFactorGraph = R"(
|
||||
size: 7
|
||||
factor 0:
|
||||
Factor 0
|
||||
GaussianFactor:
|
||||
|
||||
A[x0] = [
|
||||
10
|
||||
]
|
||||
b = [ -10 ]
|
||||
No noise model
|
||||
factor 1:
|
||||
|
||||
Factor 1
|
||||
GaussianFactor:
|
||||
|
||||
A[x1] = [
|
||||
10
|
||||
]
|
||||
b = [ -10 ]
|
||||
No noise model
|
||||
|
||||
Factor 2
|
||||
GaussianFactor:
|
||||
|
||||
A[x2] = [
|
||||
10
|
||||
]
|
||||
b = [ -10 ]
|
||||
No noise model
|
||||
|
||||
Factor 3
|
||||
HybridGaussianFactor:
|
||||
Hybrid [x0 x1; m0]{
|
||||
Choice(m0)
|
||||
0 Leaf:
|
||||
0 Leaf :
|
||||
A[x0] = [
|
||||
-1
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
|
@ -664,8 +682,9 @@ Hybrid [x0 x1; m0]{
|
|||
]
|
||||
b = [ -1 ]
|
||||
No noise model
|
||||
scalar: 0.918939
|
||||
|
||||
1 Leaf:
|
||||
1 Leaf :
|
||||
A[x0] = [
|
||||
-1
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
|
@ -674,12 +693,15 @@ Hybrid [x0 x1; m0]{
|
|||
]
|
||||
b = [ -0 ]
|
||||
No noise model
|
||||
scalar: 0.918939
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
factor 2:
|
||||
|
||||
Factor 4
|
||||
HybridGaussianFactor:
|
||||
Hybrid [x1 x2; m1]{
|
||||
Choice(m1)
|
||||
0 Leaf:
|
||||
0 Leaf :
|
||||
A[x1] = [
|
||||
-1
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
|
@ -688,8 +710,9 @@ Hybrid [x1 x2; m1]{
|
|||
]
|
||||
b = [ -1 ]
|
||||
No noise model
|
||||
scalar: 0.918939
|
||||
|
||||
1 Leaf:
|
||||
1 Leaf :
|
||||
A[x1] = [
|
||||
-1
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
|
@ -698,26 +721,21 @@ Hybrid [x1 x2; m1]{
|
|||
]
|
||||
b = [ -0 ]
|
||||
No noise model
|
||||
scalar: 0.918939
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
factor 3:
|
||||
A[x1] = [
|
||||
10
|
||||
]
|
||||
b = [ -10 ]
|
||||
No noise model
|
||||
factor 4:
|
||||
A[x2] = [
|
||||
10
|
||||
]
|
||||
b = [ -10 ]
|
||||
No noise model
|
||||
factor 5: P( m0 ):
|
||||
Choice(m0)
|
||||
0 Leaf 0.5
|
||||
1 Leaf 0.5
|
||||
|
||||
factor 6: P( m1 | m0 ):
|
||||
Factor 5
|
||||
DiscreteFactor:
|
||||
P( m0 ):
|
||||
Choice(m0)
|
||||
0 Leaf 0.5
|
||||
1 Leaf 0.5
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Factor 6
|
||||
DiscreteFactor:
|
||||
P( m1 | m0 ):
|
||||
Choice(m1)
|
||||
0 Choice(m0)
|
||||
0 0 Leaf 0.33333333
|
||||
|
|
@ -726,6 +744,7 @@ factor 6: P( m1 | m0 ):
|
|||
1 0 Leaf 0.66666667
|
||||
1 1 Leaf 0.4
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
)";
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -147,7 +147,7 @@ TEST(HybridNonlinearISAM, IncrementalInference) {
|
|||
|
||||
// Now we calculate the actual factors using full elimination
|
||||
const auto [expectedHybridBayesTree, expectedRemainingGraph] =
|
||||
switching.linearizedFactorGraph
|
||||
switching.linearizedFactorGraph()
|
||||
.BaseEliminateable::eliminatePartialMultifrontal(ordering);
|
||||
|
||||
// The densities on X(1) should be the same
|
||||
|
|
@ -214,8 +214,6 @@ TEST(HybridNonlinearISAM, ApproxInference) {
|
|||
initial.insert<double>(X(i), i + 1);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// TODO(Frank): no mode chain?
|
||||
|
||||
// Create ordering.
|
||||
Ordering ordering;
|
||||
for (size_t j = 0; j < 4; j++) {
|
||||
|
|
@ -224,7 +222,7 @@ TEST(HybridNonlinearISAM, ApproxInference) {
|
|||
|
||||
// Now we calculate the actual factors using full elimination
|
||||
const auto [unPrunedHybridBayesTree, unPrunedRemainingGraph] =
|
||||
switching.linearizedFactorGraph
|
||||
switching.linearizedFactorGraph()
|
||||
.BaseEliminateable::eliminatePartialMultifrontal(ordering);
|
||||
|
||||
size_t maxNrLeaves = 5;
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -130,7 +130,7 @@ TEST(HybridSerialization, HybridGaussianConditional) {
|
|||
// Test HybridBayesNet serialization.
|
||||
TEST(HybridSerialization, HybridBayesNet) {
|
||||
Switching s(2);
|
||||
HybridBayesNet hbn = *(s.linearizedFactorGraph.eliminateSequential());
|
||||
HybridBayesNet hbn = *(s.linearizedFactorGraph().eliminateSequential());
|
||||
|
||||
EXPECT(equalsObj<HybridBayesNet>(hbn));
|
||||
EXPECT(equalsXML<HybridBayesNet>(hbn));
|
||||
|
|
@ -141,7 +141,7 @@ TEST(HybridSerialization, HybridBayesNet) {
|
|||
// Test HybridBayesTree serialization.
|
||||
TEST(HybridSerialization, HybridBayesTree) {
|
||||
Switching s(2);
|
||||
HybridBayesTree hbt = *(s.linearizedFactorGraph.eliminateMultifrontal());
|
||||
HybridBayesTree hbt = *(s.linearizedFactorGraph().eliminateMultifrontal());
|
||||
|
||||
EXPECT(equalsObj<HybridBayesTree>(hbt));
|
||||
EXPECT(equalsXML<HybridBayesTree>(hbt));
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -26,16 +26,16 @@ namespace gtsam {
|
|||
Vector AttitudeFactor::attitudeError(const Rot3& nRb,
|
||||
OptionalJacobian<2, 3> H) const {
|
||||
if (H) {
|
||||
Matrix23 D_nRef_R;
|
||||
Matrix22 D_e_nRef;
|
||||
Unit3 nRef = nRb.rotate(bRef_, D_nRef_R);
|
||||
Vector e = nZ_.error(nRef, D_e_nRef);
|
||||
Matrix23 D_nRotated_R;
|
||||
Matrix22 D_e_nRotated;
|
||||
Unit3 nRotated = nRb.rotate(bMeasured_, D_nRotated_R);
|
||||
Vector e = nRef_.error(nRotated, D_e_nRotated);
|
||||
|
||||
(*H) = D_e_nRef * D_nRef_R;
|
||||
(*H) = D_e_nRotated * D_nRotated_R;
|
||||
return e;
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
Unit3 nRef = nRb * bRef_;
|
||||
return nZ_.error(nRef);
|
||||
Unit3 nRotated = nRb * bMeasured_;
|
||||
return nRef_.error(nRotated);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -44,8 +44,8 @@ void Rot3AttitudeFactor::print(const string& s,
|
|||
const KeyFormatter& keyFormatter) const {
|
||||
cout << (s.empty() ? "" : s + " ") << "Rot3AttitudeFactor on "
|
||||
<< keyFormatter(this->key()) << "\n";
|
||||
nZ_.print(" measured direction in nav frame: ");
|
||||
bRef_.print(" reference direction in body frame: ");
|
||||
nRef_.print(" reference direction in nav frame: ");
|
||||
bMeasured_.print(" measured direction in body frame: ");
|
||||
this->noiseModel_->print(" noise model: ");
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -53,16 +53,16 @@ void Rot3AttitudeFactor::print(const string& s,
|
|||
bool Rot3AttitudeFactor::equals(const NonlinearFactor& expected,
|
||||
double tol) const {
|
||||
const This* e = dynamic_cast<const This*>(&expected);
|
||||
return e != nullptr && Base::equals(*e, tol) && this->nZ_.equals(e->nZ_, tol)
|
||||
&& this->bRef_.equals(e->bRef_, tol);
|
||||
return e != nullptr && Base::equals(*e, tol) && this->nRef_.equals(e->nRef_, tol)
|
||||
&& this->bMeasured_.equals(e->bMeasured_, tol);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
//***************************************************************************
|
||||
void Pose3AttitudeFactor::print(const string& s,
|
||||
const KeyFormatter& keyFormatter) const {
|
||||
cout << s << "Pose3AttitudeFactor on " << keyFormatter(this->key()) << "\n";
|
||||
nZ_.print(" measured direction in nav frame: ");
|
||||
bRef_.print(" reference direction in body frame: ");
|
||||
nRef_.print(" reference direction in nav frame: ");
|
||||
bMeasured_.print(" measured direction in body frame: ");
|
||||
this->noiseModel_->print(" noise model: ");
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -70,8 +70,8 @@ void Pose3AttitudeFactor::print(const string& s,
|
|||
bool Pose3AttitudeFactor::equals(const NonlinearFactor& expected,
|
||||
double tol) const {
|
||||
const This* e = dynamic_cast<const This*>(&expected);
|
||||
return e != nullptr && Base::equals(*e, tol) && this->nZ_.equals(e->nZ_, tol)
|
||||
&& this->bRef_.equals(e->bRef_, tol);
|
||||
return e != nullptr && Base::equals(*e, tol) && this->nRef_.equals(e->nRef_, tol)
|
||||
&& this->bMeasured_.equals(e->bMeasured_, tol);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
//***************************************************************************
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -17,59 +17,69 @@
|
|||
**/
|
||||
#pragma once
|
||||
|
||||
#include <gtsam/nonlinear/NonlinearFactor.h>
|
||||
#include <gtsam/geometry/Pose3.h>
|
||||
#include <gtsam/geometry/Unit3.h>
|
||||
#include <gtsam/nonlinear/NonlinearFactor.h>
|
||||
|
||||
namespace gtsam {
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* Base class for prior on attitude
|
||||
* Example:
|
||||
* - measurement is direction of gravity in body frame bF
|
||||
* - reference is direction of gravity in navigation frame nG
|
||||
* This factor will give zero error if nRb * bF == nG
|
||||
* @class AttitudeFactor
|
||||
*
|
||||
* @brief Base class for an attitude factor that constrains the rotation between
|
||||
* body and navigation frames.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* This factor enforces that when the measured direction in the body frame
|
||||
* (e.g., from an IMU accelerometer) is rotated into the navigation frame using the
|
||||
* rotation variable, it should align with a known reference direction in the
|
||||
* navigation frame (e.g., gravity vector).
|
||||
*
|
||||
* Mathematically, the error is zero when:
|
||||
* nRb * bMeasured == nRef
|
||||
*
|
||||
* This is useful for incorporating absolute orientation measurements into the
|
||||
* factor graph.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* @ingroup navigation
|
||||
*/
|
||||
class AttitudeFactor {
|
||||
protected:
|
||||
Unit3 nRef_, bMeasured_; ///< Position measurement in
|
||||
|
||||
protected:
|
||||
|
||||
Unit3 nZ_, bRef_; ///< Position measurement in
|
||||
|
||||
public:
|
||||
|
||||
public:
|
||||
/** default constructor - only use for serialization */
|
||||
AttitudeFactor() {
|
||||
}
|
||||
AttitudeFactor() {}
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* @brief Constructor
|
||||
* @param nZ measured direction in navigation frame
|
||||
* @param bRef reference direction in body frame (default Z-axis in NED frame, i.e., [0; 0; 1])
|
||||
* @param nRef Reference direction in the navigation frame (e.g., gravity).
|
||||
* @param bMeasured Measured direction in the body frame (e.g., from IMU
|
||||
* accelerometer). Default is Unit3(0, 0, 1).
|
||||
*/
|
||||
AttitudeFactor(const Unit3& nZ, const Unit3& bRef = Unit3(0, 0, 1)) :
|
||||
nZ_(nZ), bRef_(bRef) {
|
||||
}
|
||||
AttitudeFactor(const Unit3& nRef, const Unit3& bMeasured = Unit3(0, 0, 1))
|
||||
: nRef_(nRef), bMeasured_(bMeasured) {}
|
||||
|
||||
/** vector of errors */
|
||||
Vector attitudeError(const Rot3& p,
|
||||
OptionalJacobian<2,3> H = {}) const;
|
||||
Vector attitudeError(const Rot3& p, OptionalJacobian<2, 3> H = {}) const;
|
||||
|
||||
const Unit3& nZ() const {
|
||||
return nZ_;
|
||||
}
|
||||
const Unit3& bRef() const {
|
||||
return bRef_;
|
||||
}
|
||||
const Unit3& nRef() const { return nRef_; }
|
||||
const Unit3& bMeasured() const { return bMeasured_; }
|
||||
|
||||
#ifdef GTSAM_ALLOW_DEPRECATED_SINCE_V43
|
||||
[[deprecated("Use nRef() instead")]]
|
||||
const Unit3& nZ() const { return nRef_; }
|
||||
|
||||
[[deprecated("Use bMeasured() instead")]]
|
||||
const Unit3& bRef() const { return bMeasured_; }
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
#ifdef GTSAM_ENABLE_BOOST_SERIALIZATION
|
||||
/** Serialization function */
|
||||
friend class boost::serialization::access;
|
||||
template<class ARCHIVE>
|
||||
void serialize(ARCHIVE & ar, const unsigned int /*version*/) {
|
||||
ar & boost::serialization::make_nvp("nZ_", nZ_);
|
||||
ar & boost::serialization::make_nvp("bRef_", bRef_);
|
||||
template <class ARCHIVE>
|
||||
void serialize(ARCHIVE& ar, const unsigned int /*version*/) {
|
||||
ar& boost::serialization::make_nvp("nRef_", nRef_);
|
||||
ar& boost::serialization::make_nvp("bMeasured_", bMeasured_);
|
||||
}
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
|
@ -78,12 +88,11 @@ public:
|
|||
* Version of AttitudeFactor for Rot3
|
||||
* @ingroup navigation
|
||||
*/
|
||||
class GTSAM_EXPORT Rot3AttitudeFactor: public NoiseModelFactorN<Rot3>, public AttitudeFactor {
|
||||
|
||||
class GTSAM_EXPORT Rot3AttitudeFactor : public NoiseModelFactorN<Rot3>,
|
||||
public AttitudeFactor {
|
||||
typedef NoiseModelFactorN<Rot3> Base;
|
||||
|
||||
public:
|
||||
|
||||
public:
|
||||
// Provide access to the Matrix& version of evaluateError:
|
||||
using Base::evaluateError;
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -94,23 +103,20 @@ public:
|
|||
typedef Rot3AttitudeFactor This;
|
||||
|
||||
/** default constructor - only use for serialization */
|
||||
Rot3AttitudeFactor() {
|
||||
}
|
||||
Rot3AttitudeFactor() {}
|
||||
|
||||
~Rot3AttitudeFactor() override {
|
||||
}
|
||||
~Rot3AttitudeFactor() override {}
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* @brief Constructor
|
||||
* @param key of the Rot3 variable that will be constrained
|
||||
* @param nZ measured direction in navigation frame
|
||||
* @param nRef reference direction in navigation frame
|
||||
* @param model Gaussian noise model
|
||||
* @param bRef reference direction in body frame (default Z-axis)
|
||||
* @param bMeasured measured direction in body frame (default Z-axis)
|
||||
*/
|
||||
Rot3AttitudeFactor(Key key, const Unit3& nZ, const SharedNoiseModel& model,
|
||||
const Unit3& bRef = Unit3(0, 0, 1)) :
|
||||
Base(model, key), AttitudeFactor(nZ, bRef) {
|
||||
}
|
||||
Rot3AttitudeFactor(Key key, const Unit3& nRef, const SharedNoiseModel& model,
|
||||
const Unit3& bMeasured = Unit3(0, 0, 1))
|
||||
: Base(model, key), AttitudeFactor(nRef, bMeasured) {}
|
||||
|
||||
/// @return a deep copy of this factor
|
||||
gtsam::NonlinearFactor::shared_ptr clone() const override {
|
||||
|
|
@ -123,46 +129,46 @@ public:
|
|||
DefaultKeyFormatter) const override;
|
||||
|
||||
/** equals */
|
||||
bool equals(const NonlinearFactor& expected, double tol = 1e-9) const override;
|
||||
bool equals(const NonlinearFactor& expected,
|
||||
double tol = 1e-9) const override;
|
||||
|
||||
/** vector of errors */
|
||||
Vector evaluateError(const Rot3& nRb, OptionalMatrixType H) const override {
|
||||
return attitudeError(nRb, H);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
private:
|
||||
|
||||
private:
|
||||
#ifdef GTSAM_ENABLE_BOOST_SERIALIZATION
|
||||
/** Serialization function */
|
||||
friend class boost::serialization::access;
|
||||
template<class ARCHIVE>
|
||||
void serialize(ARCHIVE & ar, const unsigned int /*version*/) {
|
||||
template <class ARCHIVE>
|
||||
void serialize(ARCHIVE& ar, const unsigned int /*version*/) {
|
||||
// NoiseModelFactor1 instead of NoiseModelFactorN for backward compatibility
|
||||
ar & boost::serialization::make_nvp("NoiseModelFactor1",
|
||||
boost::serialization::base_object<Base>(*this));
|
||||
ar & boost::serialization::make_nvp("AttitudeFactor",
|
||||
ar& boost::serialization::make_nvp(
|
||||
"NoiseModelFactor1", boost::serialization::base_object<Base>(*this));
|
||||
ar& boost::serialization::make_nvp(
|
||||
"AttitudeFactor",
|
||||
boost::serialization::base_object<AttitudeFactor>(*this));
|
||||
}
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
public:
|
||||
public:
|
||||
GTSAM_MAKE_ALIGNED_OPERATOR_NEW
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
/// traits
|
||||
template<> struct traits<Rot3AttitudeFactor> : public Testable<Rot3AttitudeFactor> {};
|
||||
template <>
|
||||
struct traits<Rot3AttitudeFactor> : public Testable<Rot3AttitudeFactor> {};
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* Version of AttitudeFactor for Pose3
|
||||
* @ingroup navigation
|
||||
*/
|
||||
class GTSAM_EXPORT Pose3AttitudeFactor: public NoiseModelFactorN<Pose3>,
|
||||
public AttitudeFactor {
|
||||
|
||||
class GTSAM_EXPORT Pose3AttitudeFactor : public NoiseModelFactorN<Pose3>,
|
||||
public AttitudeFactor {
|
||||
typedef NoiseModelFactorN<Pose3> Base;
|
||||
|
||||
public:
|
||||
|
||||
public:
|
||||
// Provide access to the Matrix& version of evaluateError:
|
||||
using Base::evaluateError;
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -173,23 +179,20 @@ public:
|
|||
typedef Pose3AttitudeFactor This;
|
||||
|
||||
/** default constructor - only use for serialization */
|
||||
Pose3AttitudeFactor() {
|
||||
}
|
||||
Pose3AttitudeFactor() {}
|
||||
|
||||
~Pose3AttitudeFactor() override {
|
||||
}
|
||||
~Pose3AttitudeFactor() override {}
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* @brief Constructor
|
||||
* @param key of the Pose3 variable that will be constrained
|
||||
* @param nZ measured direction in navigation frame
|
||||
* @param nRef reference direction in navigation frame
|
||||
* @param model Gaussian noise model
|
||||
* @param bRef reference direction in body frame (default Z-axis)
|
||||
* @param bMeasured measured direction in body frame (default Z-axis)
|
||||
*/
|
||||
Pose3AttitudeFactor(Key key, const Unit3& nZ, const SharedNoiseModel& model,
|
||||
const Unit3& bRef = Unit3(0, 0, 1)) :
|
||||
Base(model, key), AttitudeFactor(nZ, bRef) {
|
||||
}
|
||||
Pose3AttitudeFactor(Key key, const Unit3& nRef, const SharedNoiseModel& model,
|
||||
const Unit3& bMeasured = Unit3(0, 0, 1))
|
||||
: Base(model, key), AttitudeFactor(nRef, bMeasured) {}
|
||||
|
||||
/// @return a deep copy of this factor
|
||||
gtsam::NonlinearFactor::shared_ptr clone() const override {
|
||||
|
|
@ -202,40 +205,41 @@ public:
|
|||
DefaultKeyFormatter) const override;
|
||||
|
||||
/** equals */
|
||||
bool equals(const NonlinearFactor& expected, double tol = 1e-9) const override;
|
||||
bool equals(const NonlinearFactor& expected,
|
||||
double tol = 1e-9) const override;
|
||||
|
||||
/** vector of errors */
|
||||
Vector evaluateError(const Pose3& nTb, OptionalMatrixType H) const override {
|
||||
Vector e = attitudeError(nTb.rotation(), H);
|
||||
if (H) {
|
||||
Matrix H23 = *H;
|
||||
*H = Matrix::Zero(2,6);
|
||||
H->block<2,3>(0,0) = H23;
|
||||
*H = Matrix::Zero(2, 6);
|
||||
H->block<2, 3>(0, 0) = H23;
|
||||
}
|
||||
return e;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
private:
|
||||
|
||||
private:
|
||||
#ifdef GTSAM_ENABLE_BOOST_SERIALIZATION
|
||||
/** Serialization function */
|
||||
friend class boost::serialization::access;
|
||||
template<class ARCHIVE>
|
||||
void serialize(ARCHIVE & ar, const unsigned int /*version*/) {
|
||||
template <class ARCHIVE>
|
||||
void serialize(ARCHIVE& ar, const unsigned int /*version*/) {
|
||||
// NoiseModelFactor1 instead of NoiseModelFactorN for backward compatibility
|
||||
ar & boost::serialization::make_nvp("NoiseModelFactor1",
|
||||
boost::serialization::base_object<Base>(*this));
|
||||
ar & boost::serialization::make_nvp("AttitudeFactor",
|
||||
ar& boost::serialization::make_nvp(
|
||||
"NoiseModelFactor1", boost::serialization::base_object<Base>(*this));
|
||||
ar& boost::serialization::make_nvp(
|
||||
"AttitudeFactor",
|
||||
boost::serialization::base_object<AttitudeFactor>(*this));
|
||||
}
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
public:
|
||||
public:
|
||||
GTSAM_MAKE_ALIGNED_OPERATOR_NEW
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
/// traits
|
||||
template<> struct traits<Pose3AttitudeFactor> : public Testable<Pose3AttitudeFactor> {};
|
||||
|
||||
} /// namespace gtsam
|
||||
template <>
|
||||
struct traits<Pose3AttitudeFactor> : public Testable<Pose3AttitudeFactor> {};
|
||||
|
||||
} // namespace gtsam
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,136 @@
|
|||
# AttitudeFactor in GTSAM
|
||||
|
||||
[Cautionary note: this was generated from the source using ChatGPT but edited by Frank]
|
||||
|
||||
## Introduction
|
||||
|
||||
The `AttitudeFactor` in GTSAM is a factor that constrains the orientation (attitude) of a robot or sensor platform based on directional measurements. This is particularly useful in GPS-denied navigation contexts where orientation must be estimated from inertial sensors like accelerometers or magnetometers.
|
||||
|
||||
This document explains the mathematical foundation of the `AttitudeFactor` and guides users on how to use this factor effectively in GTSAM.
|
||||
|
||||
## Mathematical Foundation
|
||||
|
||||
### Concept
|
||||
|
||||
The `AttitudeFactor` constrains the rotation $\mathbf{R}_{nb}$ (from body frame $b$ to navigation frame $n$) such that a known reference direction in the navigation frame aligns with a measured direction in the body frame, when rotated. The factor enforces that:
|
||||
|
||||
$$
|
||||
\text{nRef} \approx \mathbf{R}_{nb} \cdot \text{bMeasured}
|
||||
$$
|
||||
|
||||
where:
|
||||
|
||||
- $\mathbf{R}_{nb}$ is the rotation matrix representing the orientation from body to navigation frame.
|
||||
- $\text{bMeasured}$ is the measured direction in the body frame (e.g., the accelerometer reading).
|
||||
- $\text{nRef}$ is the known reference direction in the navigation frame (e.g., the gravity vector in nav).
|
||||
|
||||
### Error Function
|
||||
|
||||
The error function computes the angular difference between the rotated reference direction and the measured direction:
|
||||
|
||||
$$
|
||||
\mathbf{e} = \text{error}(\text{nRef}, \mathbf{R}_{nb} \cdot \text{bMeasured})
|
||||
$$
|
||||
|
||||
This error is minimal (zero) when the rotated body reference direction aligns perfectly with the measured navigation direction.
|
||||
|
||||
The error is computed internally using the `attitudeError` function:
|
||||
|
||||
```cpp
|
||||
Vector AttitudeFactor::attitudeError(const Rot3& nRb) const {
|
||||
Unit3 nRotated = nRb * bMeasured_;
|
||||
return nRef_.error(nRotated);
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### Explanation:
|
||||
- The function computes the rotated measurement `nRotated` and then the error between `nRef` and `nRotated`.
|
||||
- `nRef_.error(nRotated)` is a 2D vector-valued error between two directions, defined in [Unit3.h](../geometry/Unit3.h).
|
||||
|
||||
### Jacobians
|
||||
|
||||
For optimization, the $2 \times 3$ Jacobian of the error function with respect to the rotation parameters is required. The Jacobian is computed using chain rule differentiation, involving the derivative of the rotated vector with respect to the rotation parameters and the derivative of the error with respect to the rotated vector.
|
||||
|
||||
Note the Jacobian for this specific error function vanishes 180 degrees away from the true direction, and the factor is only expected to behave well when the `nRb` value is initialized in the correct hemisphere.
|
||||
|
||||
## Usage in GTSAM
|
||||
|
||||
### Including the Header
|
||||
|
||||
Include the `AttitudeFactor.h` header in your code:
|
||||
|
||||
```cpp
|
||||
#include <gtsam/navigation/AttitudeFactor.h>
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Creating an Attitude Factor
|
||||
|
||||
You can create an attitude factor for either a `Rot3` (rotation only) or a `Pose3` (position and rotation) variable.
|
||||
|
||||
#### For `Rot3` Variables
|
||||
|
||||
```cpp
|
||||
// Define keys
|
||||
gtsam::Key rotKey = ...;
|
||||
|
||||
// Known reference direction in navigation frame (e.g., gravity)
|
||||
gtsam::Unit3 nRef(0, 0, -1); // Assuming gravity points down in navigation frame
|
||||
|
||||
// Measured direction in body frame (e.g., accelerometer direction)
|
||||
gtsam::Unit3 bMeasured(0, 0, 9.8); // will be normalized automatically
|
||||
|
||||
// Noise model
|
||||
auto noiseModel = gtsam::noiseModel::Isotropic::Sigma(2, 0.1); // 2D error, sigma = 0.1
|
||||
|
||||
// Add to factor graph
|
||||
gtsam::NonlinearFactorGraph graph;
|
||||
graph.emplace_shared<Rot3AttitudeFactor>(rotKey, nRef, noiseModel, bMeasured);
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### For `Pose3` Variables
|
||||
|
||||
There is also a `Pose3AttitudeFactor` that automatically extracts the rotation from the pose, taking into account the chain rule for this operation so the Jacobians with respect to pose are correct.
|
||||
The same caveat about vanishing Jacobian holds.
|
||||
|
||||
```cpp
|
||||
// Define keys
|
||||
gtsam::Key poseKey = ...;
|
||||
|
||||
// Known reference direction in navigation frame (e.g., gravity)
|
||||
gtsam::Unit3 nRef(0, 0, -1); // Assuming gravity points down in navigation frame
|
||||
|
||||
// Measured direction in body frame (e.g., accelerometer direction)
|
||||
gtsam::Unit3 bMeasured(0, 0, 9.8); // will be normalized automatically
|
||||
|
||||
// Noise model
|
||||
auto noiseModel = gtsam::noiseModel::Isotropic::Sigma(2, 0.1);
|
||||
|
||||
// Add to factor graph
|
||||
gtsam::NonlinearFactorGraph graph;
|
||||
graph.emplace_shared<Pose3AttitudeFactor>(poseKey, nRef, noiseModel, bMeasured);
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Explanation of Parameters
|
||||
|
||||
- **Key**: The variable key in the factor graph corresponding to the `Rot3` or `Pose3` variable you are constraining.
|
||||
- **nRef**: The known direction in the navigation frame. This is typically obtained from sensors like accelerometers or magnetometers.
|
||||
- **bMeasured**: The measured direction in the body frame. By default, this is set to the Z-axis `[0; 0; 1]`, but it should match the direction your sensor measures. When constructing a `Unit3`, will be automatically normalized.
|
||||
- **noiseModel**: The noise model representing the uncertainty in the measurement. Adjust the standard deviation based on the confidence in your measurements.
|
||||
|
||||
## Example in GPS-Denied Navigation
|
||||
|
||||
In GPS-denied environments, orientation estimation relies heavily on inertial measurements. By incorporating the `AttitudeFactor`, you can:
|
||||
|
||||
- Constrain the roll and pitch angles using gravity measurements from an accelerometer.
|
||||
- Constrain the yaw angle using magnetic field measurements from a magnetometer (with caution due to magnetic disturbances).
|
||||
|
||||
This factor helps maintain an accurate orientation estimate over time, which is crucial for applications like drone flight, underwater vehicles, or indoor robotics.
|
||||
|
||||
## Conclusion
|
||||
|
||||
The `AttitudeFactor` is a useful tool in GTSAM for incorporating orientation measurements into your factor graph. By aligning a measured direction in the body frame with a known reference direction in the navigation frame, it provides a constraint that improves the estimation of the rotation variable. Correct understanding and usage of this factor enhance the performance of navigation algorithms, especially in challenging environments where GPS is unavailable.
|
||||
|
||||
# References
|
||||
|
||||
- [GTSAM Documentation](https://gtsam.org/)
|
||||
- [Unit3 Class Reference](https://gtsam.org/doxygen/)
|
||||
|
|
@ -37,13 +37,9 @@ typedef ManifoldPreintegration PreintegrationType;
|
|||
|
||||
/*
|
||||
* If you are using the factor, please cite:
|
||||
* L. Carlone, Z. Kira, C. Beall, V. Indelman, F. Dellaert, "Eliminating
|
||||
* conditionally independent sets in factor graphs: a unifying perspective based
|
||||
* on smart factors", Int. Conf. on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), 2014.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* C. Forster, L. Carlone, F. Dellaert, D. Scaramuzza, "IMU Preintegration on
|
||||
* Manifold for Efficient Visual-Inertial Maximum-a-Posteriori Estimation",
|
||||
* Robotics: Science and Systems (RSS), 2015.
|
||||
* Christian Forster, Luca Carlone, Frank Dellaert, and Davide Scaramuzza,
|
||||
* "On-Manifold Preintegration for Real-Time Visual-Inertial Odometry", IEEE
|
||||
* Transactions on Robotics, 2017.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* REFERENCES:
|
||||
* [1] G.S. Chirikjian, "Stochastic Models, Information Theory, and Lie Groups",
|
||||
|
|
@ -54,8 +50,8 @@ typedef ManifoldPreintegration PreintegrationType;
|
|||
* [3] L. Carlone, S. Williams, R. Roberts, "Preintegrated IMU factor:
|
||||
* Computation of the Jacobian Matrices", Tech. Report, 2013.
|
||||
* Available in this repo as "PreintegratedIMUJacobians.pdf".
|
||||
* [4] C. Forster, L. Carlone, F. Dellaert, D. Scaramuzza, "IMU Preintegration on
|
||||
* Manifold for Efficient Visual-Inertial Maximum-a-Posteriori Estimation",
|
||||
* [4] C. Forster, L. Carlone, F. Dellaert, D. Scaramuzza, "IMU Preintegration
|
||||
* on Manifold for Efficient Visual-Inertial Maximum-a-Posteriori Estimation",
|
||||
* Robotics: Science and Systems (RSS), 2015.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,42 @@
|
|||
# Navigation Factors
|
||||
|
||||
This directory contains factors related to navigation, including various IMU factors.
|
||||
|
||||
## IMU Factor:
|
||||
|
||||
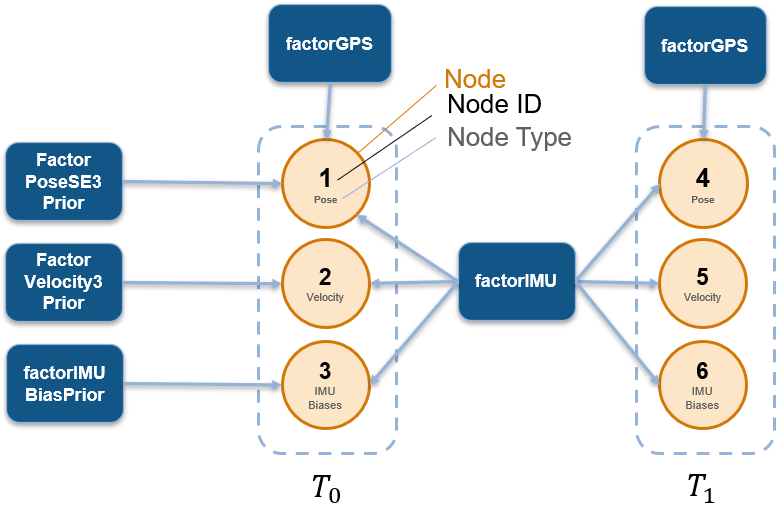
|
||||
|
||||
The `ImuFactor` is a 5-ways factor involving previous state (pose and velocity of
|
||||
the vehicle at previous time step), current state (pose and velocity at
|
||||
current time step), and the bias estimate.
|
||||
Following the preintegration
|
||||
scheme proposed in [2], the `ImuFactor` includes many IMU measurements, which
|
||||
are "summarized" using the PreintegratedIMUMeasurements class.
|
||||
The figure above, courtesy of [Mathworks' navigation toolbox](https://www.mathworks.com/help/nav/index.html), which are also using our work, shows the factor graph fragment for two time slices.
|
||||
|
||||
Note that this factor does not model "temporal consistency" of the biases
|
||||
(which are usually slowly varying quantities), which is up to the caller.
|
||||
See also `CombinedImuFactor` for a class that does this for you.
|
||||
|
||||
If you are using the factor, please cite:
|
||||
> Christian Forster, Luca Carlone, Frank Dellaert, and Davide Scaramuzza, "On-Manifold Preintegration for Real-Time Visual-Inertial Odometry", IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 2017.
|
||||
|
||||
## REFERENCES:
|
||||
1. G.S. Chirikjian, "Stochastic Models, Information Theory, and Lie Groups",
|
||||
Volume 2, 2008.
|
||||
2. T. Lupton and S.Sukkarieh, "Visual-Inertial-Aided Navigation for
|
||||
High-Dynamic Motion in Built Environments Without Initial Conditions",
|
||||
TRO, 28(1):61-76, 2012.
|
||||
3. L. Carlone, S. Williams, R. Roberts, "Preintegrated IMU factor:
|
||||
Computation of the Jacobian Matrices", Tech. Report, 2013.
|
||||
Available in this repo as "PreintegratedIMUJacobians.pdf".
|
||||
4. C. Forster, L. Carlone, F. Dellaert, D. Scaramuzza, "IMU Preintegration on
|
||||
Manifold for Efficient Visual-Inertial Maximum-a-Posteriori Estimation",
|
||||
Robotics: Science and Systems (RSS), 2015.
|
||||
|
||||
## The Attitude Factor
|
||||
|
||||
The `AttitudeFactor` in GTSAM is a factor that constrains the orientation (attitude) of a robot or sensor platform based on directional measurements. Both `Rot3` and `Pose3` versions are available.
|
||||
|
||||
Written up in detail with the help of ChatGPT [here](AttitudeFactor.md).
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -256,34 +256,30 @@ virtual class AHRSFactor : gtsam::NonlinearFactor {
|
|||
};
|
||||
|
||||
#include <gtsam/navigation/AttitudeFactor.h>
|
||||
//virtual class AttitudeFactor : gtsam::NonlinearFactor {
|
||||
// AttitudeFactor(const Unit3& nZ, const Unit3& bRef);
|
||||
// AttitudeFactor();
|
||||
//};
|
||||
virtual class Rot3AttitudeFactor : gtsam::NonlinearFactor{
|
||||
Rot3AttitudeFactor(size_t key, const gtsam::Unit3& nZ, const gtsam::noiseModel::Diagonal* model,
|
||||
const gtsam::Unit3& bRef);
|
||||
Rot3AttitudeFactor(size_t key, const gtsam::Unit3& nZ, const gtsam::noiseModel::Diagonal* model);
|
||||
virtual class Rot3AttitudeFactor : gtsam::NoiseModelFactor {
|
||||
Rot3AttitudeFactor(size_t key, const gtsam::Unit3& nRef, const gtsam::noiseModel::Diagonal* model,
|
||||
const gtsam::Unit3& bMeasured);
|
||||
Rot3AttitudeFactor(size_t key, const gtsam::Unit3& nRef, const gtsam::noiseModel::Diagonal* model);
|
||||
Rot3AttitudeFactor();
|
||||
void print(string s = "", const gtsam::KeyFormatter& keyFormatter =
|
||||
gtsam::DefaultKeyFormatter) const;
|
||||
bool equals(const gtsam::NonlinearFactor& expected, double tol) const;
|
||||
gtsam::Unit3 nZ() const;
|
||||
gtsam::Unit3 bRef() const;
|
||||
gtsam::Unit3 nRef() const;
|
||||
gtsam::Unit3 bMeasured() const;
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
virtual class Pose3AttitudeFactor : gtsam::NonlinearFactor {
|
||||
Pose3AttitudeFactor(size_t key, const gtsam::Unit3& nZ,
|
||||
virtual class Pose3AttitudeFactor : gtsam::NoiseModelFactor {
|
||||
Pose3AttitudeFactor(size_t key, const gtsam::Unit3& nRef,
|
||||
const gtsam::noiseModel::Diagonal* model,
|
||||
const gtsam::Unit3& bRef);
|
||||
Pose3AttitudeFactor(size_t key, const gtsam::Unit3& nZ,
|
||||
const gtsam::Unit3& bMeasured);
|
||||
Pose3AttitudeFactor(size_t key, const gtsam::Unit3& nRef,
|
||||
const gtsam::noiseModel::Diagonal* model);
|
||||
Pose3AttitudeFactor();
|
||||
void print(string s = "", const gtsam::KeyFormatter& keyFormatter =
|
||||
gtsam::DefaultKeyFormatter) const;
|
||||
bool equals(const gtsam::NonlinearFactor& expected, double tol) const;
|
||||
gtsam::Unit3 nZ() const;
|
||||
gtsam::Unit3 bRef() const;
|
||||
gtsam::Unit3 nRef() const;
|
||||
gtsam::Unit3 bMeasured() const;
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
#include <gtsam/navigation/GPSFactor.h>
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -11,44 +11,44 @@
|
|||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* @file testAttitudeFactor.cpp
|
||||
* @brief Unit test for Rot3AttitudeFactor
|
||||
* @brief Unit test for AttitudeFactors (rot3 and Pose3 versions)
|
||||
* @author Frank Dellaert
|
||||
* @date January 22, 2014
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
#include <gtsam/navigation/AttitudeFactor.h>
|
||||
#include <CppUnitLite/TestHarness.h>
|
||||
#include <gtsam/base/Testable.h>
|
||||
#include <gtsam/base/numericalDerivative.h>
|
||||
#include <gtsam/navigation/AttitudeFactor.h>
|
||||
|
||||
#include <functional>
|
||||
|
||||
#include "gtsam/base/Matrix.h"
|
||||
#include <CppUnitLite/TestHarness.h>
|
||||
|
||||
using namespace std::placeholders;
|
||||
using namespace std;
|
||||
using namespace gtsam;
|
||||
|
||||
// *************************************************************************
|
||||
TEST( Rot3AttitudeFactor, Constructor ) {
|
||||
|
||||
TEST(Rot3AttitudeFactor, Constructor) {
|
||||
// Example: pitch and roll of aircraft in an ENU Cartesian frame.
|
||||
// If pitch and roll are zero for an aerospace frame,
|
||||
// that means Z is pointing down, i.e., direction of Z = (0,0,-1)
|
||||
Unit3 bZ(0, 0, 1); // reference direction is body Z axis
|
||||
Unit3 nDown(0, 0, -1); // down, in ENU navigation frame, is "measurement"
|
||||
Unit3 bMeasured(0, 0, 1); // measured direction is body Z axis
|
||||
Unit3 nDown(0, 0, -1); // down, in ENU navigation frame, is "reference"
|
||||
|
||||
// Factor
|
||||
Key key(1);
|
||||
SharedNoiseModel model = noiseModel::Isotropic::Sigma(2, 0.25);
|
||||
Rot3AttitudeFactor factor0(key, nDown, model);
|
||||
Rot3AttitudeFactor factor(key, nDown, model, bZ);
|
||||
EXPECT(assert_equal(factor0,factor,1e-5));
|
||||
Rot3AttitudeFactor factor(key, nDown, model, bMeasured);
|
||||
EXPECT(assert_equal(factor0, factor, 1e-5));
|
||||
|
||||
// Create a linearization point at the zero-error point
|
||||
Rot3 nRb;
|
||||
EXPECT(assert_equal((Vector) Z_2x1,factor.evaluateError(nRb),1e-5));
|
||||
EXPECT(assert_equal((Vector)Z_2x1, factor.evaluateError(nRb), 1e-5));
|
||||
|
||||
auto err_fn = [&factor](const Rot3& r){
|
||||
auto err_fn = [&factor](const Rot3& r) {
|
||||
return factor.evaluateError(r, OptionalNone);
|
||||
};
|
||||
// Calculate numerical derivatives
|
||||
|
|
@ -80,32 +80,31 @@ TEST(Rot3AttitudeFactor, CopyAndMove) {
|
|||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// *************************************************************************
|
||||
TEST( Pose3AttitudeFactor, Constructor ) {
|
||||
|
||||
TEST(Pose3AttitudeFactor, Constructor) {
|
||||
// Example: pitch and roll of aircraft in an ENU Cartesian frame.
|
||||
// If pitch and roll are zero for an aerospace frame,
|
||||
// that means Z is pointing down, i.e., direction of Z = (0,0,-1)
|
||||
Unit3 bZ(0, 0, 1); // reference direction is body Z axis
|
||||
Unit3 nDown(0, 0, -1); // down, in ENU navigation frame, is "measurement"
|
||||
Unit3 bMeasured(0, 0, 1); // measured direction is body Z axis
|
||||
Unit3 nDown(0, 0, -1); // down, in ENU navigation frame, is "reference"
|
||||
|
||||
// Factor
|
||||
Key key(1);
|
||||
SharedNoiseModel model = noiseModel::Isotropic::Sigma(2, 0.25);
|
||||
Pose3AttitudeFactor factor0(key, nDown, model);
|
||||
Pose3AttitudeFactor factor(key, nDown, model, bZ);
|
||||
EXPECT(assert_equal(factor0,factor,1e-5));
|
||||
Pose3AttitudeFactor factor(key, nDown, model, bMeasured);
|
||||
EXPECT(assert_equal(factor0, factor, 1e-5));
|
||||
|
||||
// Create a linearization point at the zero-error point
|
||||
Pose3 T(Rot3(), Point3(-5.0, 8.0, -11.0));
|
||||
EXPECT(assert_equal((Vector) Z_2x1,factor.evaluateError(T),1e-5));
|
||||
EXPECT(assert_equal((Vector)Z_2x1, factor.evaluateError(T), 1e-5));
|
||||
|
||||
Matrix actualH1;
|
||||
|
||||
auto err_fn = [&factor](const Pose3& p){
|
||||
auto err_fn = [&factor](const Pose3& p) {
|
||||
return factor.evaluateError(p, OptionalNone);
|
||||
};
|
||||
// Calculate numerical derivatives
|
||||
Matrix expectedH = numericalDerivative11<Vector,Pose3>(err_fn, T);
|
||||
Matrix expectedH = numericalDerivative11<Vector, Pose3>(err_fn, T);
|
||||
|
||||
// Use the factor to calculate the derivative
|
||||
Matrix actualH;
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -21,6 +21,8 @@
|
|||
#include <gtsam/base/Manifold.h>
|
||||
#include <gtsam/nonlinear/NonlinearOptimizer.h>
|
||||
|
||||
#include <stdexcept>
|
||||
|
||||
namespace gtsam {
|
||||
|
||||
/// Fletcher-Reeves formula for computing β, the direction of steepest descent.
|
||||
|
|
@ -247,6 +249,9 @@ std::tuple<V, int> nonlinearConjugateGradient(
|
|||
case DirectionMethod::DaiYuan:
|
||||
beta = DaiYuan(currentGradient, prevGradient, direction);
|
||||
break;
|
||||
default:
|
||||
throw std::runtime_error(
|
||||
"NonlinearConjugateGradientOptimizer: Invalid directionMethod");
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
direction = currentGradient + (beta * direction);
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue